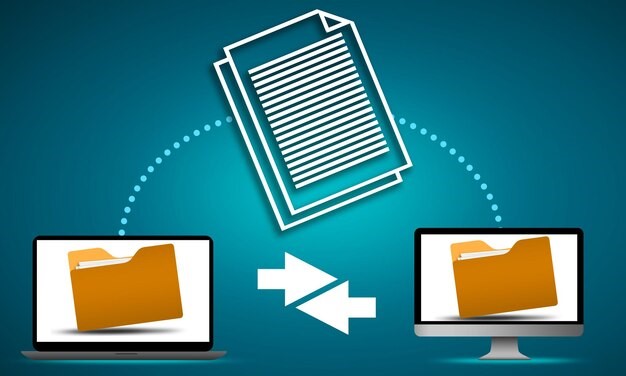
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format) is a versatile image format widely used by artists, photographers, and designers for its ability to store high-quality, uncompressed images. Unlike JPEGs or PNGs, TIFF files maintain their fidelity and allow for intricate edits without compromising detail. These attributes make them an excellent choice for artwork, whether digital or printed.
However, the large file size and complex nature of TIFF files can make them challenging to work with, especially for online sharing or efficient storage. Optimising your TIFF files ensures they retain their quality while becoming more practical for diverse applications. This guide provides actionable tips to help artists and designers prepare their TIFF files for professional use, whether it’s for galleries, clients, or online portfolios.
Understanding the Importance of TIFF Files in Artwork
- Uncompromised Image Quality
TIFF files are renowned for their lossless compression, meaning no data is lost during saving or editing. This makes them ideal for artwork that requires precision, such as high-resolution scans of paintings or intricate digital illustrations.
Unlike formats like JPEG, which can degrade over time with repeated edits, TIFF preserves the integrity of your file. For artists who regularly revisit their work for adjustments, this is a crucial advantage.
- Versatility Across Platforms
TIFF files are compatible with a variety of software, including Adobe Photoshop, CorelDRAW, and even CAD tools. This versatility makes them a preferred format for artists who need to transition between different programs during the creative process.
Moreover, TIFF files can store multiple layers and transparency, giving artists the flexibility to experiment with complex designs or retouch their work without losing crucial elements.
- Print and Digital Excellence
For printed artwork, TIFF files ensure your colours, gradients, and details are rendered accurately. Their ability to support CMYK colour profiles makes them a standard in professional printing. On the digital side, optimised TIFFs can be converted into other formats for sharing, ensuring your audience experiences the full impact of your art.
Steps to Optimise TIFF Files for Artwork
- Choose the Right Resolution
The resolution of your TIFF file determines its clarity and detail. While higher resolutions are desirable for prints, they can lead to unnecessarily large file sizes for digital purposes.
- For print: Aim for a resolution of 300 DPI (dots per inch). This standard ensures sharp and professional-quality prints, especially for posters or gallery pieces.
- For digital use: Reduce the resolution to 72 DPI. This setting is sufficient for screens and reduces the file size significantly without sacrificing too much visible detail.
- Compress Without Compromising Quality
Although TIFF files are typically uncompressed, they do support lossless compression methods like LZW (Lempel-Ziv-Welch) and ZIP. These options reduce the file size while maintaining the original image quality.
When saving your TIFF file in your editing software, choose the compression option that best suits your needs. LZW is widely supported and works well for images with fewer colour variations, while ZIP offers better compression for complex designs.
- Optimise Layers and Transparency
While layers and transparency add flexibility during editing, they can also inflate your file size. Before finalising your TIFF, merge unnecessary layers or flatten the image if you no longer need to edit its components.
For designs requiring transparency, ensure you’re saving in a format compatible with your intended use. Some printing services or software might not fully support TIFF transparency, so it’s worth confirming beforehand.
- Adjust Colour Profiles
Using the correct colour profile ensures your artwork looks consistent across devices and prints. For digital artwork, the RGB profile is standard, while CMYK is essential for print.
When optimising a TIFF for print, calibrate your monitor and select a CMYK profile that aligns with your printer’s specifications. This step minimises discrepancies in colour output, preserving the integrity of your artwork.
Best Practices for Managing TIFF Files
- Create Backup Copies
Before optimising your TIFF file, always save a backup of the original. This precaution ensures you can return to the unaltered version if something goes wrong during editing or compression.
Cloud storage platforms like Google Drive or OneDrive are excellent for storing your backups securely. They also enable easy access to your files from multiple devices.
- Organise Your Files
Given the large size of TIFF files, an organised folder structure is essential for efficient management. Label your files clearly, indicating details like version numbers, resolution, or intended use (e.g., “Artwork_Name_300DPI_Print”).
Using dedicated software or metadata tags can also help you categorise and search for your files quickly.
- Test Before Finalising
Before sharing or printing your optimised TIFF file, test it on various devices and platforms. For example, view it on different screens to ensure colour consistency or print a small section to verify resolution and detail.
Converting TIFF Files for Sharing
Although TIFF is an excellent format for working with artwork, its large file size and specialised nature make it less ideal for sharing. Converting TIFF files to lighter formats like JPEG or PNG is a common solution.
- JPEG: Best for sharing previews or uploading to social media, where smaller file sizes are essential.
- PNG: Ideal for digital portfolios that require transparency or high-quality visuals.
- PDF: Suitable for client presentations or archiving multiple TIFF images in a single file.
Online tools such as ImagesLite make converting TIFF files quick and straightforward while maintaining quality.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-compressing Files
While compression is beneficial for reducing file size, excessive compression can result in artefacts or loss of detail. Always preview your file after compression to ensure the quality meets your standards.
- Ignoring File Compatibility
Not all software or printers fully support TIFF features like layers or transparency. Test your optimised file in its intended environment to avoid compatibility issues.
- Skipping Metadata Updates
Metadata stores crucial information about your TIFF file, such as its creation date, resolution, and colour profile. Neglecting to update this data can lead to confusion or mismanagement, especially for large collections of artwork.
Optimising TIFF files for artwork ensures they are versatile, high-quality, and practical for various uses, from professional printing to online sharing. By managing resolution, compression, and colour profiles effectively, you can maximise the impact of your creations while maintaining efficiency.
For quick and reliable TIFF optimisation or conversion, consider using ImagesLite. With user-friendly features and high-quality output, ImagesLite makes it easy to prepare your TIFF files for any artistic endeavour. Try it today to streamline your creative workflow!